Also known as “politicians discussing climate change”
Blog 4 on Post Covid disruption, resilience and innovation.
This blog will explore the role of the government and how it needs to change to be effective in the ‘living with Covid’ or ‘post Covid’ world.
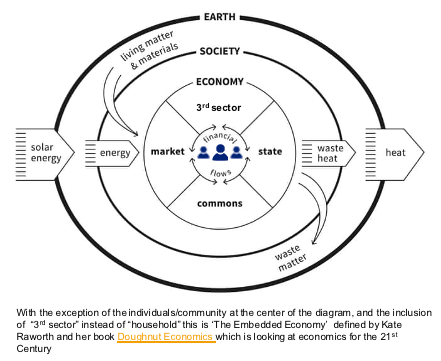
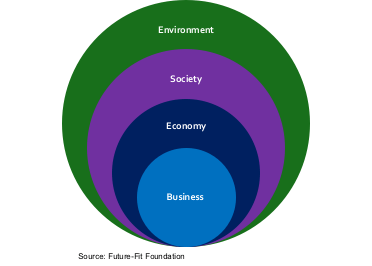
As I have talked about in other blogs, the context to talk about the governments role is against an individual centric world, which is not a company or government centric view. Individuals are the building blocks of societies. As depicted in Figure 4-1, from the individual in the centre there are concentric circles going out for the economy, society and the environment. Defining the social contract between individuals and their societies, or countries, sets the parameters within which the different actors must operate and the goals they must strive to achieve. The actors are the market economy, the government, the 3rd sector, and the public themselves. For a longterm sustainable world there must also be a social contract with the earth. We must live within the resource constraints and operating system of the earth to keep it in balance – clearly an area where we are currently failing at on most fronts. Finally, this model implies that the sum of the country/societal models rolls up into an aggregated view which then ideally operates sustainably from an earth and climate viewpoint.
The role of the government (the state) that I refer to is against the the model of advanced countries, which are both democratic and market economy driven. Against almost any set of comparative measures analysing country performance, these two factors are key descriptors of success. It is worth noting Winston Churchill’s famous quote on democracy, “No one pretends that democracy is perfect or all-wise. Indeed it has been said that democracy is the worst form of Government except for all those other forms that have been tried from time to time”. The majority of what I discuss would apply in different forms to all countries.
To start, one of the key questions is what is government for? Lee Kuan Yew, Prime Minister of Singapore from 1959 to 1990, stated, “the ultimate test of the value of a political system is whether that society establish conditions that improve the standard of living for the majority of its people. He always stated that the proof is in the pudding; rising incomes for the broad middle class, health, security and economic opportunity. Based on the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), I would overlay onto this the concept of social inclusiveness on core human rights. These rights would include minimum rights related to income, shelter and food; equal access to quality health and education; equal treatment, rights and opportunity; and, freedom of speech and movement.
Based on this definition, we can all see shortcomings in our own countries. This pandemic along with other challenges, including economic, the ‘black lives matter’ and ‘me too’ movements, and the climate and environmental challenges bring to light shortcomings.
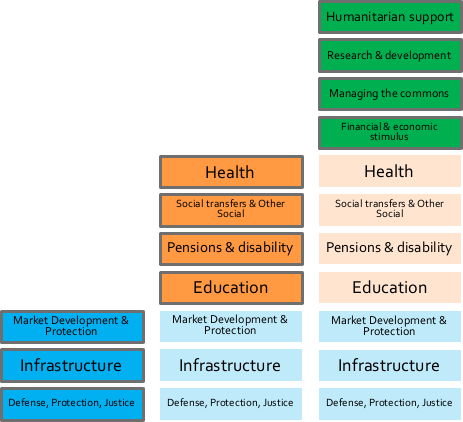
It is worth looking at what the roles of the government are in the advanced countries (Figure 4-2). Broadly, there are three different sets of activities. The first set are core roles typically linked to the base functioning of a country. The second set are government roles associated with the provision of public services to individuals. The final set are roles linked to the goal of contributing to the development and stability of the economy and protection of the environment. Not all advanced countries effectively cover all these roles. For example, the US does not have universal healthcare and the provision of education to all children is highly imbalanced.
Effective government is complex and challenging at the best of times. We all worry about whether or not the government is focused on the right things, whether or not they are spending their money wisely against the priorities they have set, and what is the true impact of their spend versus the rhetoric we hear.
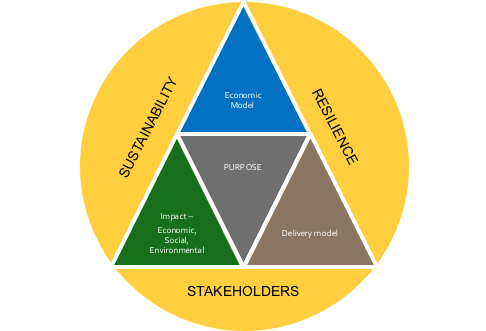
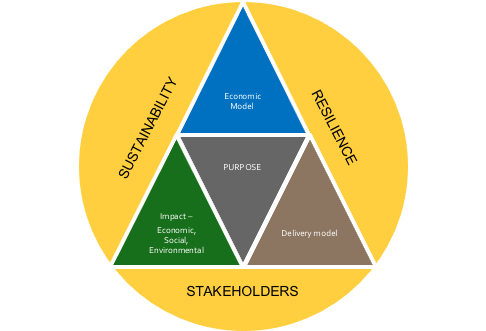
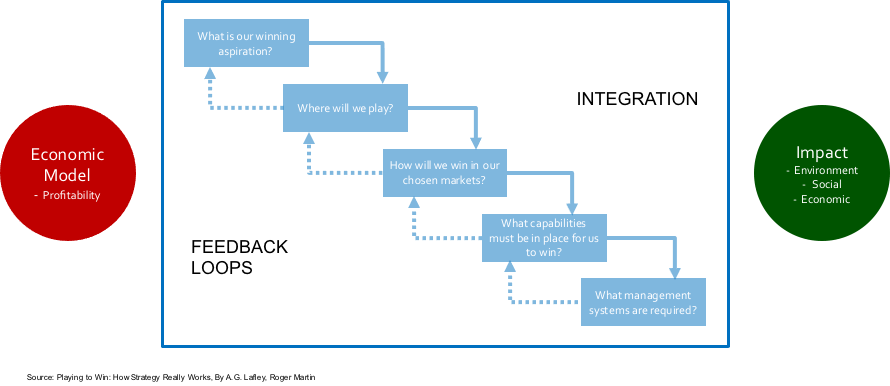
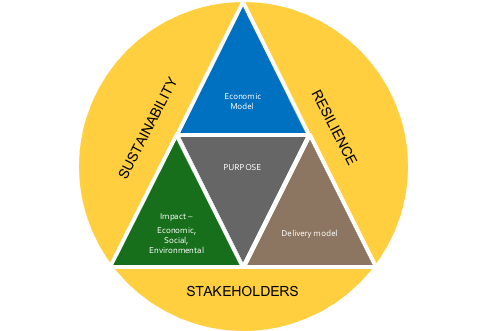
As I see it, and have noted before, the strategic framework that I set out for businesses is also the same framework for the government (Figure 4-3). This is required of a system based framework.
For each role of the government, it ideally should be able to define the economic, social and environmental impact they want to achieve, the delivery model for achieving the impact and the way that it is financed fiscally and/or through debt financing. Wouldn’t it be great to have a government report card against each of its roles so that there was clear accountability!
The pandemic has affected all parts of the governments in most countries in profound ways. Healthcare, welfare and education systems have been deeply affected, tested and come up short in many ways. Public transport systems usage has collapsed. Police forces and the military have been asked to perform different tasks. The levels of economic support provided and demanded are at unprecedented levels. The level of cross border cyber attacks have grown. The need for multi-lateral coordination has increased. And, the list goes on!
As we move, to ‘living with Covid’ and, hopefully then a post-Covid world, reverting to governments previous modus operandi will not be adequate in most countries. There are also other large disruptive factors that have not been effectively addressed; these include, climate change, social fairness and growing geo-political tensions; and in each country, they will have their own additional lists, such as Brexit for the UK. All of this creates a complex cocktail of challenges for governments to focus on going forward.
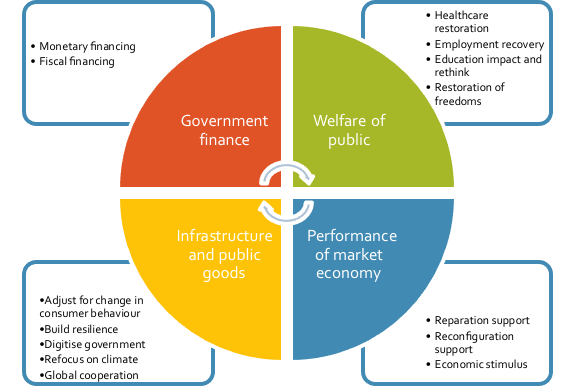
There are four overall areas for the government to think about (Figure 4-4). Firstly, their role in the welfare of the public, their key constituent. This includes being ready for the next equivalent pandemic, making sure that at all times normal medical treatment can be provided, and solving how to continually improve the quality of healthcare services with an ageing population and tight financial requirements.
There are big concerns over the quality and impact of education during Covid. There is a lot of work to do in understanding digital education delivery and putting in capabilities for either fully remote delivery (for emergencies) or ongoing hybrid education. The opportunity should also be taken to see how education impact can be enhanced vs. the current normal in-person education delivery.
Restoration of freedoms. The pandemic has resulted in significant restrictions on individuals and in many cases undue use of private information. There have been losses of freedom of movement and of socialisation. There have been restrictions on the ability to work with remote working being mandated in many areas. Many countries have put in curfews in locations with high outbreaks. Last but not least, in a number of countries, individuals have had to sign up to apps so that the health authorities can track their movement. There have been requisite loss of freedoms for businesses and organistions to operate. Eliminations of these restrictions and restoration of normal rights is a critical part of moving to a new normal; no one wants a full time ‘nanny state’.
In addition, across all parts of the government, they can make a big impact by ensuring the optimum levels of employment in the supply chains related to their services; this includes, having a careful look at the role of local vs. international sourcing.
Secondly, restoring the performance of the market economy. Universally, the performance of the market economy is the key driver to economic growth and the improvement of the welfare of the population of a country. One of the key roles of the government in advanced economies has been to reduce the impact of a recession and contribute to its rebound – economic smoothing. In the post pandemic environment, this includes helping sound economic companies and sectors to recover; looking at challenged sectors and thinking how to assist them in reconfiguring into a successful relevant sector going forward; and, providing stimulus in the form of research and development, and financial support, to key strategic and growth sectors going forward – including driving the green agenda.
Thirdly, investing in infrastructure and public goods to get them appropriately focused for impact going forward and to improve employment levels. With a ‘new normal’ being driven off changes in consumer behaviour, the government needs to incorporate this into the specific requirements and capacities needed for each service they provide. There is also a period of excess resources required for catch up in areas such as the health sector where diagnosis of ailments and treatments have lagged during the crisis.
Building resilience against future disruptions (including pandemics, fires, flood, tornados, etc.) should also not be forgotten. It is very clear that a number of countries were highly unprepared for a pandemic despite everyone knowing that it was a possibility. Just look at the preparedness of countries such as S Korea, Singapore, Japan and Germany and the superior outcomes they have achieved vs. the woeful performance of the US, UK, Spain, Belgium and many South American countries among others who were caught unprepared.
Linked to resilience is the need to shift services to include the use of digital capabilities to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of service delivery as well as resilience. Improved administration efficiency, digital and hybrid healthcare and education delivery are other clear areas. Japan, under its new prime minister, Yoshihide Suga, has just announced a minister responsible for the digitisation of government services.
The other area governments should look at is bringing forward investments that create a multiplier effect on employment and the economy. Climate change is one of these areas, where accelerated investment is critical in any event to help countries meet their Paris Climate Agreement commitments. As with this pandemic, climate change also demands each of the governments to improve levels of global cooperation. Global problems need global solutions.
There are limits to investment capacity, so governments need to make tough choices on where to focus their efforts and then what combinations of the 3 Fs (frameworks, financing and fiscal) they use to stimulate the market economy. Frameworks are regulations and other non-financial mechanisms that the governments put in place to shape markets, drive consumer behaviour, deliver public services and protect individuals and organisations. Clearly, financing and fiscal are the financial mechanisms for funding different activities. To the extent that the government can find ways to help the economy recover without always reverting to financing, then we are all ultimately better off. This could be as simple as re-zoning roads to provide plenty of room for outdoor seating for cafes and restaurants to help them rebuild their businesses.
One of the leading modern economists, Mariana Mazzucato, has been pushing to create/recreate dynamic public-private interaction and the creation of mission oriented industrial strategies. She clearly identifies that the state is instrumental in many parts of our economy, including helping to stabilise and grow the economy, yet the spoils of their involvement is never appropriately compensated vs. the risk. Virtually all the upside where the government is assisting accrues to businesses and their shareholders despite the public (through taxes) taking the risk. Whether the government is helping businesses to recover, helping sectors to reconfigure or stimulating the growth of new sectors, through R&D or investment, the government should be looking for a fair reward structure for their successful involvement. This should help reduce a governments debt burden, and the consequent public tax burden, over time. It should also help drive improved corporate responsibility.
In summary, for each government this is a complex equation of where to spend and how much. The three categories of potential spend are addressing fundamental shortfalls in public services, providing market economy recovery and growth support, and bringing forward government programs that will create a job multiplier effect. Some example areas are shown in Figure 4-5.
Integral to the development of a ‘new normal’ is also a society aligned with accelerating progress against our critical environmental challenges of addressing climate change and biodiversity. Clear focused programs on these must be included. As an example see Figure 4-6.
Behind all these factors and potential initiatives to restore and progress economies, is the simple truth that uncertainty is the enemy of progress. Having clarity on government actions and programs, confidence that they won’t unsuspectingly change and some forms of longer term certainty that individuals and the market economy can plan on and rely on is critical. This gives individuals and companies confidence, horizons they can plan against, and an improved ability to raise further financing.
#Covid 19 #pandemic #post Covid #strategy #disruption #resilience #innovation #WHO #McKinsey #Accenture #EY #UN SDGs #WEF #blacklivesmatter #metoo #DoughnutEconomics @Kate Raworth @Mariana Mazzucato #biodiversity #remote working #strategic framework #climate change #government role #social contract #public #infrastructure #fiscal policy #monetary policy