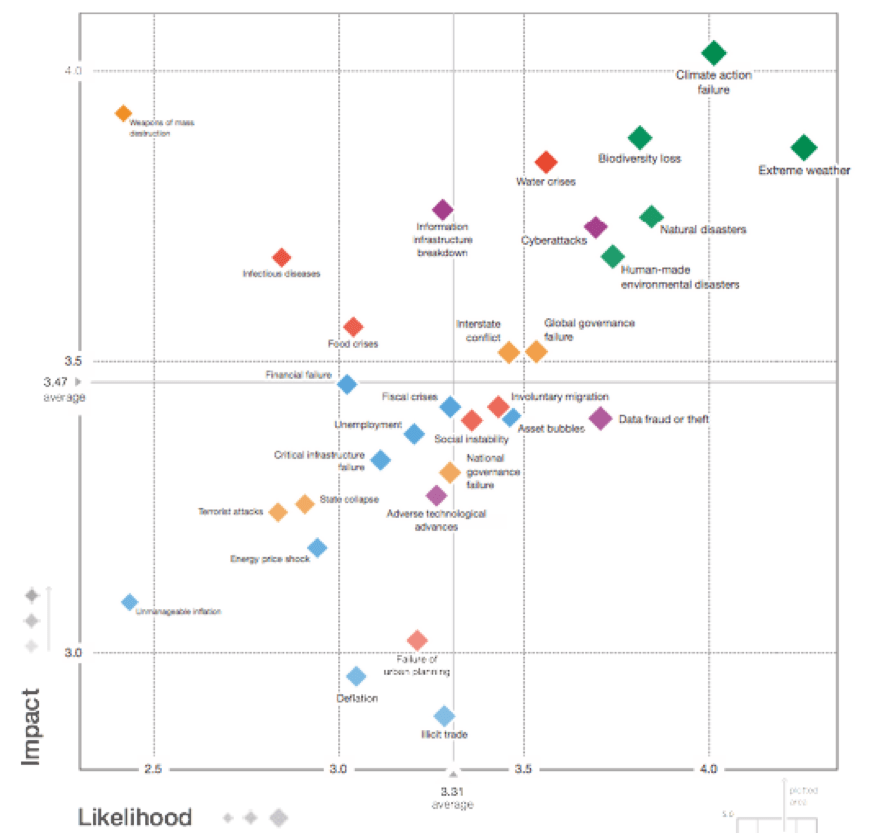
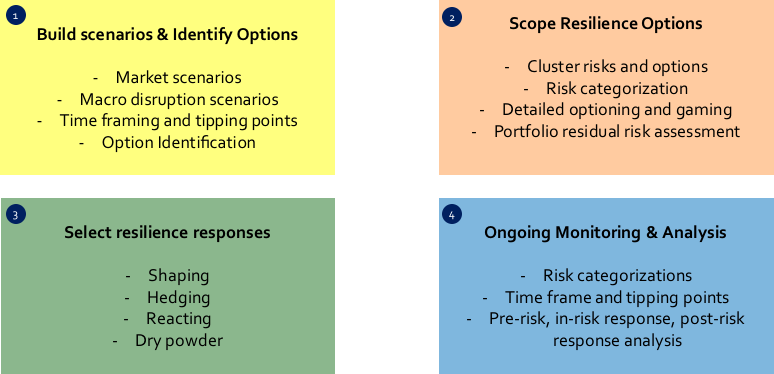
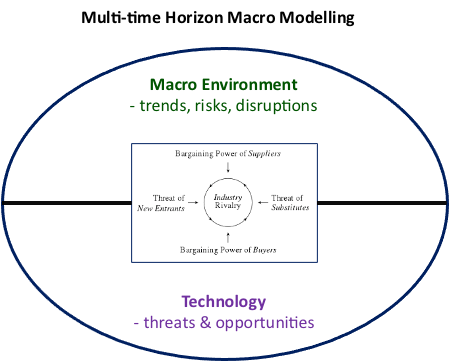
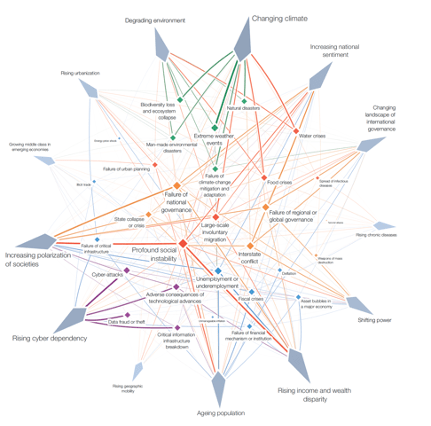
Blog 3 on Post Covid disruption, resilience and innovation.
In the last blog, we talked about changes to consumer behaviour as a result of our current and ongoing Covid experience. Whether we end up living with Covid or are living in a post Covid vaccinated world, consumer behaviour will have changed.
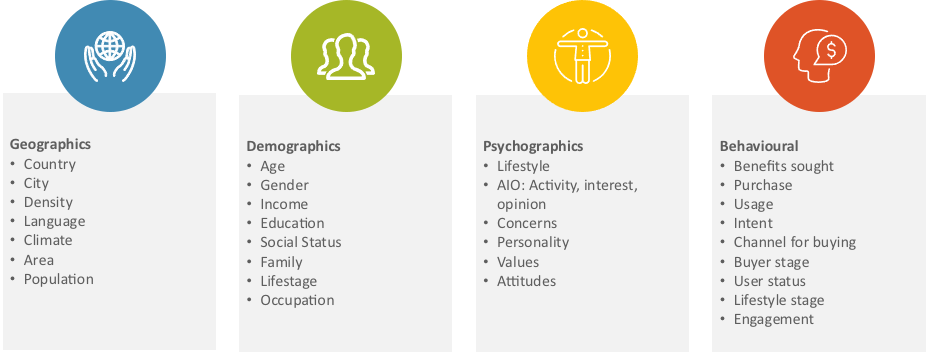
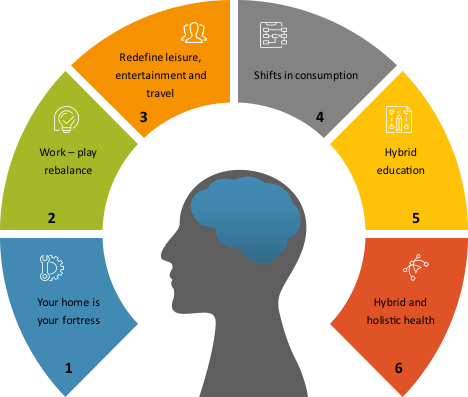
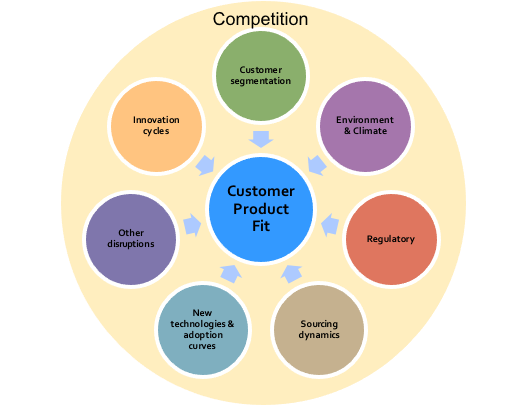
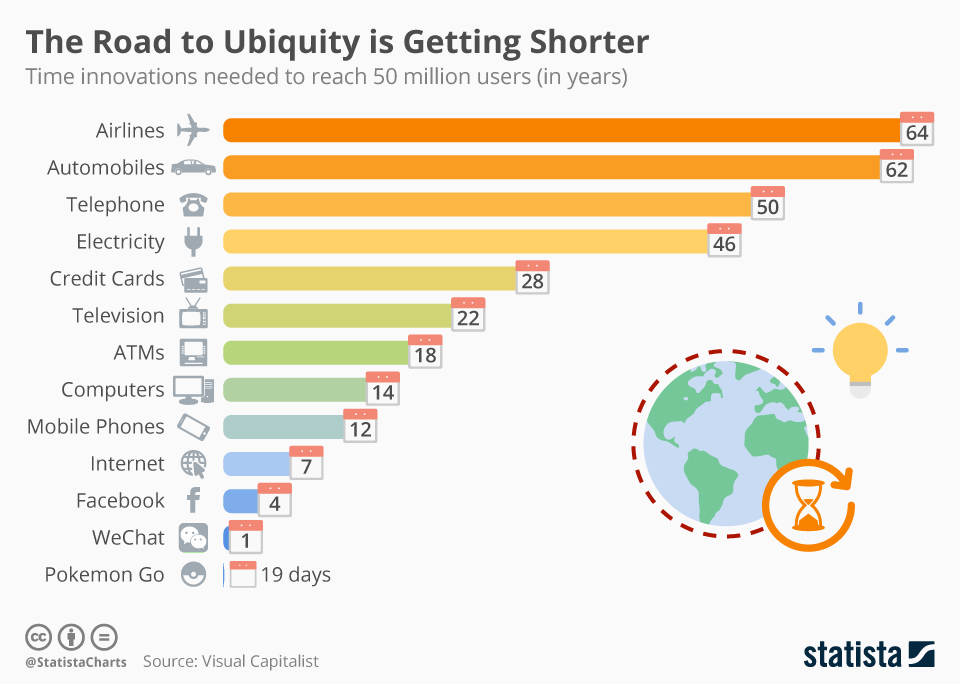
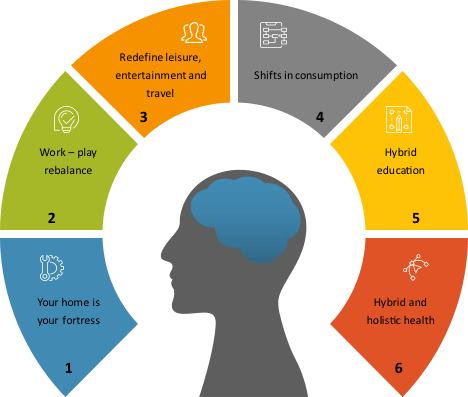
Six areas of likely change were identified, see Figure 3-1 and described in more detail in Blog 2, although the scale of these changes are not clear and will vary across countries and customer segments within a country.
The drivers of these changes from the Covid experience to date are:
- Structural responses by businesses to Covid. For example, policy shifts by companies towards remote working will make changes to consumer spending and ripple through to the retail and service sector around offices.
- Structural responses by governments. For example, rules and regulations on crowds and distancing, or adjustments related to public transport and other types of infrastructure.
- Behavioural changes linked to actual and perceived health risks of consumers
- Behavioural changes linked to economic changes and uncertainties to large sets of consumers
- Changes in the attitudes of sets of people with respect to buying locally as a response to seeing local economic distress in combination with a sense of social responsibility and increased climate change concerns
- Responses by the government to address potential future health challenges and alleviate the economic recession we have entered. As an example, this would include accelerated investment in moving a country towards ‘greening’ the economy and society.
- The increased rate of change of adoption of existing technology applications and introduction of new technology applications
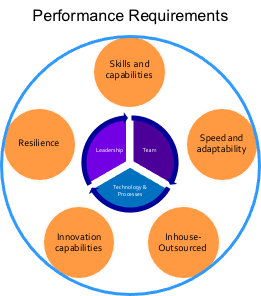
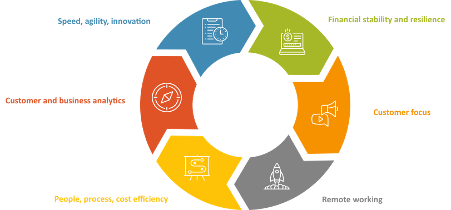
For business, to continue to deal with the Covid crisis, emerge stronger and be on top of these changes there are 6 aspects to running a business that should be top of mind (Figure 3-2). These components are valid for both consumer and B2B businesses.
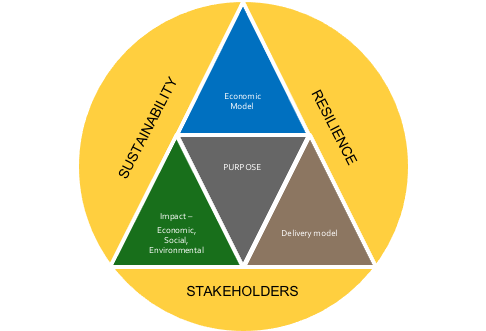
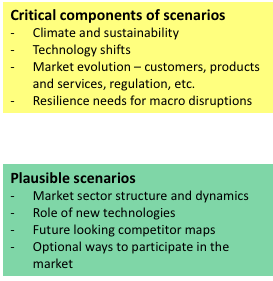
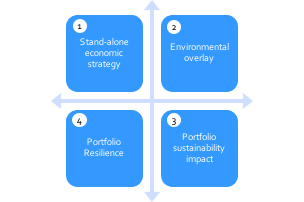
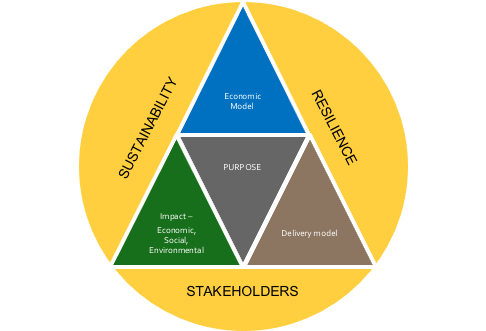
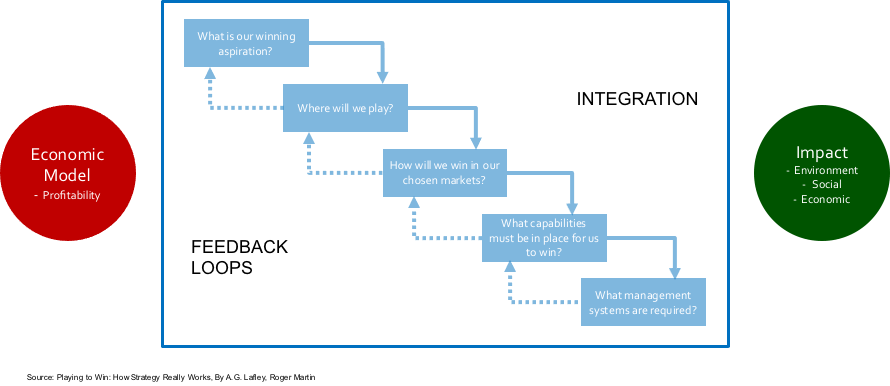
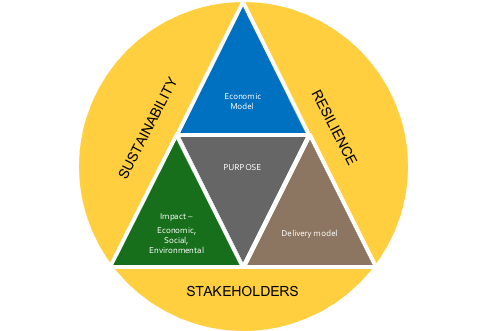
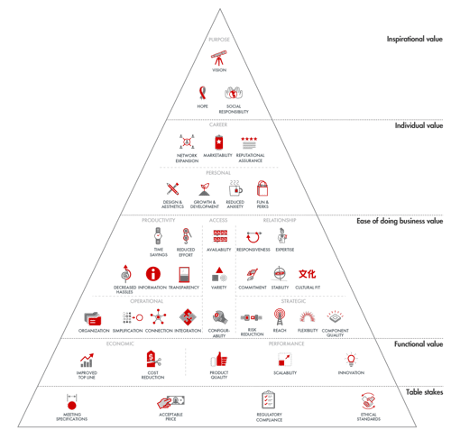
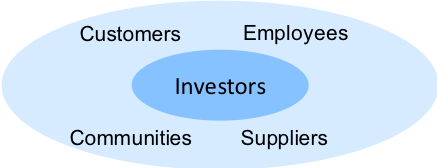
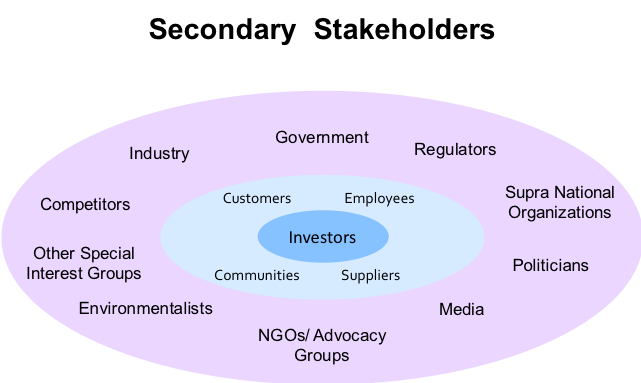
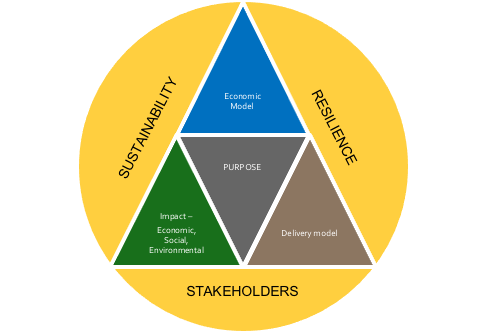
Before we explore the six areas, it is vital that a company does not lose sight of its strategy and what it is trying to accomplish. In my previous series of business strategy, I introduced what I believe is the right strategic framework for the future (Figure 3-3). Having a business purpose that is focused on delivering both a return to investors and a combination of economic, social and environmental impact, is what captures hearts and minds. Engaging the hearts and minds of employees, participants in your supply chain and customers contributes to higher levels of performance and resilience in challenging times. A strategy is also a guiding light around which the changes you need to make and initiatives you need to deliver sit. You want to build a strong business for the medium-long term not just survive the short term!
Let’s now explore each of the six activities to help identify opportunities to move forward more effectively. Six months into Covid and I am sure that many businesses are well on the way to making changes and adjusting to a ‘new normal’. I hope some of these factors will add to your plans.
Starting with financial stability and resilience, there are 3 areas of particular focus that I want to address (Figure 3-4).

Cash is king – For companies that have real concerns about survival, the most important first thing to do is to switch from a prime focus on profitability to a core focus on cash. This combines the focus on revenue and costs with the timing of receipts and payments. Structurally changing the amount of working capital needed in the business can often free up the cash needed to get through difficult times. It also helps a company look in more detail on the specifics of what they are spending their money on, making better decisions on the amount and timing of product purchases for inventory, and the need for new assets and how they might be paid for, such as a rent or a lease vs. outright purchase.
The classic approach to this is to do a 13 week rolling cashflow plus 9 rolling months (12 months in total). To get really focused and extract the most value from this approach the cashflow should be updated on a weekly basis or at least every 2 weeks.
Finance for resilience – If your cash position is not strong and you cannot cover the business challenges through an extended period of time then finding new financing should be a priority. Although in general equity is preferable to debt in times of high uncertainty, if debt is the only answer then you should be looking at increasing your cash position to give plenty of headroom. Remember a bird in the hand is worth more than two in the bush. Banks are notorious for lending you an umbrella when it is sunny and taking it away when it starts to rain; so, be very focused on both the terms of repayment and any covenants on the debt. Before locking in any agreements, be sure there is understanding on the implications of what has been agreed against different challenging scenarios.
If equity is an option, then in general raise a large amount so that there is headroom for a long time and you can ride through potential challenging fundraising times at a later date. It will also allow you to rapidly take advantage of future challenges your competitors may have or aggressively pursue new opportunities. Having too much cash on the balance sheet in the current times is a high class problem!
Scenario Plan – In these times of pandemic disruption, we are now in a non-linear period of change. Extrapolating historic revenue trends is an insufficient approach to financial planning. Building alternative scenarios is the only way. Scenarios should particularly focus on identifying where you might hit critical performance/survival points and what contingency plans need to be in place and triggered as you move towards these points. Creating scenarios over a broad range of outcomes is an essential part of being able to rapidly react to different performance paths, because time is money.
Customer focus is the next area to look at (Figure 3-5) as having a clear approach for efficiently optimising your revenues and contribution is mission critical.

Customers First – If the company has been suffering during the pandemic and the challenge is to get back towards old levels of revenues as soon as possible then getting the most cost efficient approach to recovering revenues is what you are trying to accomplish. The simple way to think of customers is that there are three core categorisations to think about – customers, dormant customers and prospects. Customers are those that you currently consider to be ongoing customers and would often be defined as having done business with in the last 12 months. Dormant customers are those that were former customers but are now inactive; consistent with the definition above of customers, these would be customers who have been inactive for at least 12 months. Prospects are potential customers you have never done business with before.
The economics of revenue generation are very different by each of the groups with existing customers being by far the best economically and prospects being the worst. It is true to say that the best way to grow revenues is by first optimising the retention and growth of existing customers. Having to replace customers to stand still is not efficient. Mass product marketing, and not using customer data, will tend to be far less efficient for many businesses.
The likely customer response rates to sales and marketing initiatives are driven by 6 core variables to start with (Figure 3-6). As a company builds experience with targeting, modelling response rates and measuring real results, there should be continuous refinement of the variables.

Recency, frequency and monetary value (RFM) looks at the currency and loyalty of a customer. A recent high volume and long term high value customer is the most likely customer to buy from you. For high value – high potential response customers you should be willing to invest more to get them to buy product. For example, you may do a telephone call to high value customers; but, it would be prohibitively expensive to cold call low value dormant customers.
For marketing specific products, you also want to consider channel affinity, timing and product affinity. Channel affinity is the channels of communication and sales channels that have worked in the past with a specific customer. Timing is critical to consider as for example, a product may be seasonal or have specific renewal timing (eg. insurance products). Product affinity is the definition of how close the product you are trying to sell is to historic products that the customer has bought. The closer the affinity, the higher the likely response rates.
For both existing customers and dormant customers personalisation of messaging, offers and promotions will drive up response rates. To drive up the sales value of customers from previous levels you ideally want to know what ‘share of wallet’ you have vs. their full potential with you. This can also be done by evaluating whether low value customers ‘look alike’ with some high value spenders. If you have emails for all customers, subject to GDRP restrictions, then this is an essential low cost communications channel for both existing customers and dormant customers; however, this does not necessarily mean that you should not spend some money to engage in additional ways with high value customers.
For new customers, or prospects, different sales and marketing activities are required. The choice of approach should be linked to the historic cost of customer acquisition and subsequent customer profitability of different sets of activities. It may well be that mass marketing is more efficient than specific targeted marketing at specific prospect segments. If you are doing targeted marketing, then it is valuable to try and profile the characteristics of potential new customers vs. the characteristics of current high value customers (‘look alike’ modelling).
If you have been doing this for some time, with well structured test and control techniques, then you should already be well down the road to efficiently rebuilding your revenues.
Reward Loyalty – In this context, this is about looking for ways to lock in revenue streams for an extended period of time and/or generate pre-purchase revenues to enhance the cashflow and the amount and reliability of future revenue streams. This is effectively looking at alternative business models that will improve your cashflows. You can look at Blog 9 in my Business Strategy series to look at this in more depth. One example of this would be to provide discounts/benefits for minimum levels of pre-payment for future purchases. For example, the Starbucks card generates upfront cash for subsequent use by customers. An alternative example would be to convert an upfront payment to a locked in minimum period of monthly payments. A final example would be to offer a full year’s subscription to a service at a discounted upfront payment vs. the sum of 12 monthly payments. These all can drive improved and/or more reliable cashflows and potentially improve customer retention rates and average revenues per customer.
Listen to Customers – When your business is going non-linear through dramatic shifts in consumer behaviour change – buying habits, use of on-line, and a changing mix of how your customers are spending – then in depth listening to customers on a continuous basis is essential to be able to catch and react to changes as soon as possible. You should use a combination of surveys and in depth discussions to really understand what is driving the changes. The conversations will help you to frame potential changes/solutions to these behavioural changes as well as making your communications more contextually relevant and effective.
Innovate to Retain – With large consumer behavioural changes, more marketing and better messaging alone will not be enough. To retain and grow revenues, innovation across a number of dimensions may well be necessary – channels to market, pricing, packaging, product, services and promotion. Fast effective innovation needs time and attention, robust testing and evaluation, and resource commitment; it should not be an add on to teams that already have a full workload. If you need new skills sets that are not available internally, outsource to make sure that you start well down the experience curve; this is especially important if for the first time you are moving to on-line selling and marketing.
Remote working is a vital capability for flexibility and to be able to always operate. The pandemic has highlighted this. No company can afford to be without this capability. I have identified 3 key areas to highlight (Figure 3-7).
Shift to Hybrid/Remote Working – Remote or hybrid working is not new. Since the beginning of the digital era, the shift started with sales teams, outsourcing services and online selling. Many companies realised that if you move to flexible workspace and allowed some remote work that you only need about 65% of the desks and generate huge savings on office space. The pandemic has made companies realise that remote working is also a resilience capability.
The pandemic has also helped companies test which activities work effectively remotely and which ones don’t. In general, it seems that all types of creative work can be much more effective in person and socialisation between people is an integral part of building effective working relationships. Of course, from a human perspective there are lots of other dimensions that need to be evaluated from the convenience and saving of commuting time, to the inherent need of all of us for socialisation and to the higher challenges of the lower income employees who have less space at home to be able to have a productive working space.
If employees need to work from home then the company needs to ensure that they are equipped to do so with mobile phone, portable computers and screens, adequate internet etc. and, if necessary, adequate space to work. Behind these capabilities for individuals is often the need for a set of team based tools that share calendars, improve productivity and communications, track output and ensure security of data. Solving the ecosystem of how the business works effectively remotely is critical.
Move to the Cloud and SAAS – The cloud and SAAS (software a a service) are great enablers for businesses today. They are the core enablers of enterprise wide hybrid and remote working. You can reduce the need for large tech teams to run your IT infrastructure and variabilise your costs and as we well as adding remote capabilities. Why not allow experts at storage and retrieval, and experts with intensive sector wide applications worry about the applications for non differentiating parts of your businesss in a way that you could not afford to do.
Almost all large companies, that have not already switched, will have a ‘not invented here’ issue with their tech teams and be defending their realm. In a few cases, their in-house systems may drive competitive advantages; but, in most cases it is the fear of change and the idea of technical debt arresting progress rather than the potential benefits of new applications. Do you really think that internally you can build a better cloud at a lower full cost than Amazon, Microsoft, Google and IBM? And, do you think that you can build a better set of customer facing application than Salesforce.com for example? Have a look at their development budgets that you are competing against. Many of these cloud and SAAS applications have already built integrations between them, so the prime focus of attention is the setup, and in some cases customisation, of the solutions to get the full business benefits.
Test and Learn – Going remote may sound easy and it’s just about technology; however, this is all about trying the create the right set up to optimise the interaction of people within the business and with other key third parties. The goal should be to create a new level of performance and not just replicate the in-office approach to work. The measures of success aren’t just on short term performance and productivity measures, the new way of working must also outperform in attracting and retaining the best employees. The company needs to test and learn to find the right people processes and the right tools. The processes need to include the right daily interactions, both task and social oriented, and involve the right tools (eg. Slack) for communicating and interacting.
People, process, and cost efficiency need close scrutiny when a business takes a revenue hit and the dynamics of doing business change. It is essential to see how to offset the revenue hit and shift to the right capabilities going forward. Figure 3-8 identifies three areas to cover off.

It is easy to ‘slash and burn’ costs and forget about everything else if you are in fear of failing; however, it is useful to be clear on why the company was successful up to the time of the pandemic. Inevitably, it included a combination of the people, the culture and the processes, among other things, that got you there. Don’t forget, it is many of the current components that will also help you to rebound. I also encourage you to consider how to minimise the social cost you may generate by how you address the short term challenges. We all need to face up to the economic, social and environmental challenges around us and do our part.
Share the Pain – Philosophically and practically, each company lives within an ecosystem. That ecosystem involves the company, and all the parts within that organism, and all the other interrelated companies in the supply chain and support sectors. At the extreme for example, if you are running a ‘just in time’ manufacturing operation, then you are completely reliant on the supply side from raw materials to components moving through the supply chain to time; and, if anything disrupts this timing then your business suffers. Against this context of an ecosystem, then any cost reduction activities needs to also consider the implications across the performance of the ecosystem.
When you are looking at cost reduction opportunities, you need to look at all the places that costs can either be taken out, reduced or renegotiated. Depending on how you approach this you can win or lose friends in this process. Maintaining trust, respect and loyalty from those in the business and those you do business with is a key part of the decision making. This is where ‘sharing the pain’ comes in. If people see that the pain is being shared and thoughtfully distributed rather than inflicted on an easy victim you will often be better off. The ruthless exercise of power over a weaker but important supplier does not translate to long term loyalty and reliability; however, displaying an understanding of their situation and trying to solve the problem in a constructive way does.
In the same way, with the potentially devastating impact on certain people from the loss of employment, agreeing that everyone will take a short term pay cut to preserve employment and allow the company to rebound more effectively may be a better answer to dismissals. Shared pay cuts should ideally come in the form of higher pay cuts to the higher paid, or at least the executive teams, whose lives are less affected – this is leadership and an understanding of social impact!
Understand Mission Critical – As businesses evolve in good economic times, it is easy to be less focused on understanding the full relationship of incurring additional costs and the related benefits to revenue and profits. There tends to be a growing pool of ‘nice to have’ vs. ‘need to have’ activities.
In challenging times, getting back to the basics is essential. Start by being very clear on what is critical to attracting and retaining customers, and ideally growing the revenue per customer. With this in mind, then the best way to do this, with the least negative impact, is through process mapping to simplify, speed up, reduce waste, reduce process breakdowns and cut costs. This is the constructive approach to cost cutting.
Leverage with Technology – Across all processes, it is worth looking at where technology could fit and what SAAS (software as a service) applications could be used. The goal is to explore reductions in time, improvements in quality, and reductions in human involvement. There is every reason to believe that there are opportunities in all functional areas. They can range from scanning invoices and automating entry into accounting systems, chatbots and customer self service opportunities, tools for customer relationship management and automated marketing, project management software, HR applications, etc. Many people will be surprised at the extent of opportunities to automate and improve processes with technology.
Customer and business analytics are most valuable in times of change. They should be embedded in how a company works. There is a lot of talk about KPI’s, balanced scorecards and customer analytics; however, too many companies fall short of what is really required. Every year, the ability to generate or collect information so that a business can be run on facts improves. The faster you receive information the faster you can make informed decisions. There are four key topics (Figure 3-9) to cover off that really make the difference.

KPI Driven – Over time I have seen too many companies at the executive level over focus on financial based data; yet, the financial data is the outcome of customer, operational, process, and HR based activities. To take decisions, key information needs to be linked to the root cause of what needs to be managed. Building effective dashboards is not easy but it is invaluable. Cascading down KPI’s is what helps create the linkages between decisions at the top and impact at the coal face.
Continuous Market Analysis – In challenging and uncertain times, being on top of shifts in consumption and customer behaviour and then being able to react is essential. Being able to discern seasonal variations and general volatility from new trends in consumption is the critical skill. This is often helped by active discussions and feedback from customers and prospects.
Integrate with Rapid Decision Cycles – Analysis without consequent decision making has little value. As an example, in the retail fashion sector in the early 1990s many product and sourcing decisions were made typically at least 12 months before the start of the season. Then Gap innovated to move to 6 week cycles of decision making with the finalising of product and volume decisions much closer to the period; and now, Zara can turn around product within 2 weeks to take advantage of in season trends. This type of capability transforms the performance of a business by ensuring the business is not laden with excess inventory, minimising lost sales by taking advantage of high selling items and adding new high selling product in season. Think about the analogies to this in your business.
Speed, agility and innovation is what underpins a company’s ability to react in difficult times and succeed over time. The four components to examine are set out in Figure 3-10. In technology companies, we continuously witness updates in applications and the developments of whole new versions of software and hardware. With Apple, we are on iPhone 11, Apple Watch Series 6, and the Mac OS Catalina soon to be Big Sur. An ability to continuously raise the bar on what you deliver to customers keeps competitors chasing you rather than the other way round. Businesses in all sectors need these capabilities.

Shift to Agile Management – Agile project management is the most common way that companies undertake software development. It is an iterative development methodology of breaking down development into discrete sets of deliverables, often with a time frame of about 2 weeks, that rapidly speed up development. It also more often than not, does not require the full definition of the end product; rather, that becomes clearer as the team goes through each cycle and incorporates continuous learning related to the end product or service.
The concept of running a whole business also on rapid cycles with clearly defined deliverables is gaining steam. It creates a winning mindset and approach to the business by a management team that is so much more powerful than a standard monthly routine. In some businesses, such as certain retail sectors, it may be better to run on weekly cycles in certain parts of the business.
Fact based decision making – There is no reason to make decisions without facts anymore. That is not to say that you do not also overlay judgements based on analysis of the future. Facts include both internal information and external information (customer, market, competitor, etc.). The critical point to focus on is that agile management requires very current feedback; and in times of great change, such as these, external dynamics can shift very quickly. Just as in retail, you need to be able to identify the hot new products, brands, and shifts in purchasing focus as early as possible. Trying to save money by using less current external information is usually a ‘false economy’.
Stand Alone Innovation Team – In my experience, from running many companies, effective innovation can only be achieved with proper resource dedication and commitment. Without resourcing away from the black hole of day to day management and challenges, the speed of innovation is inevitably compromised. Innovation needs to be seen as mission critical as day to day performance.
Learning Curve Driven – ‘Fail fast’ is the common phrase for companies that are truly learning curve driven. The faster you learn the quicker you can go down the learning curve. This is an essential part of smaller companies outperforming larger slower companies. To effectively learn and push the envelope further and faster culturally, it must be acceptable to fail and not a negative on a person’s performance.
Leadership sits on top of the drive to change, the sets of market initiatives you pursue, and the new capabilities you put in place. The key mindset is to see the unsettling of markets and operations as an opportunity. Leadership needs to think like an attacker not and incumbent. They need to be thinking about new opportunities, new markets, new ways of doing things, new applications of technology and leading with empathy and inclusion. For most people, change is uncomfortable; however, for leadership it needs to become a way of life and a challenge you look forward to conquer.
The next blog, will explore the implications for governments of the post Covid, or living with Covid world.
#Covid 19 #pandemic #post Covid #strategy #disruption #resilience #innovation #consumer segmentation #consumer behaviour #GenZ #millenials #baby boomers #WHO #sustainable development goals #McKinsey #Accenture #EY #UN SDGs #WEF #blacklivesmatter #metoo #DoughnutEconomics @Kate Raworth #agile #test and learn #cloud #SAAS #process efficiency #CRM #customer retention #remote working #strategic framework #climate change