Jess Conrad
Blog 2 on Post Covid disruption, resilience and innovation.
Covid 19 is raising lots of questions about the future. The most prescient questions are related to solving this health crisis. Most importantly, is when will there be a vaccine ready for use and/or how can we live with Covid 19 and have a relatively normal way of life without economic disruption. The second set of questions relate to what life might look like when it gets more normalised, and in what way will this Covid experience have changed our environment and changed us to create a ‘new normal’. The third set of questions are related to how companies need to adjust what they are doing to manage through the crisis and be successful going forward. Finally, how must the government adjust their priorities to help the people and the economy recover and be ready to effectively face the challenges going forward.
The debate is well underway and will continue for many years on how each country has dealt with the crisis, what was successful, what was not and what are the critical lessons that we must address to be more effective in future pandemic situations. At the end of the day each country has chosen a path heavily based on ‘science’, as they claim, and this had resulted in a mix of responses in terms of the level of lockdown, the rate and approach to opening up, the response to new outbreaks, the use of masks and highly variable economic responses. Clearly, the science is not clear and nor are the appropriate responses health wise, economically or politically. We can only hope that through the diversity of responses that we will take advantage of this, look at the facts, compare the outcomes from multiple perspectives and do a dramatically better job next time.
So how have our lives changed and what are the components of a ‘new normal’ way of life for living with Covid or post Covid?
To think about consumer behaviour, it is useful to start by looking generally at consumer segmentation and then we can explore how behaviour might change against those segmentations as a result of the current Covid experience.
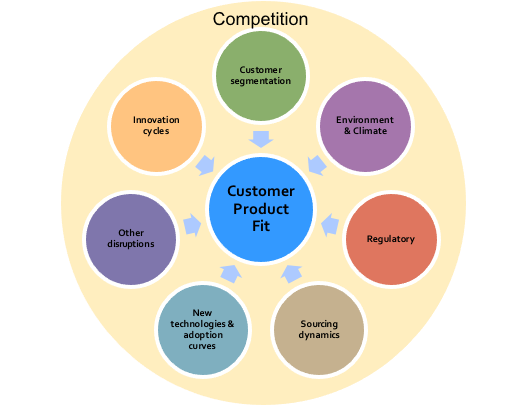
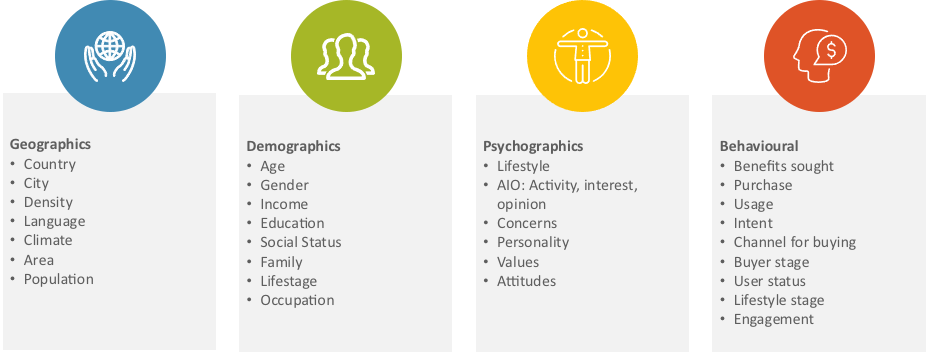
As an initial context, it is worth quickly visiting what components make up and drive consumer segmentation. There are four categories of factors that drive consumption and buying behaviour (Figure 2-1) – geographics, demographics, psychographics, behavioural. From analysing customer behaviour with data on these factors, clusters of common behaviours can be identified and then used to target and market to the relevant customers for a consumer business. There are equivalent techniques that are used in business to business.
If you just look at these factors and reflect on your Covid experience you will see that there are inevitable changes to consumer behaviour post Covid. There will have been changes in a broad cross section of areas including:
- the income of many people
- the potential need to look at alternative occupations
- changes in attitudes to health and economic risk
- adjustments to lifestyle priorities
- changes to how you work and the level of commuting you do
- changes to where and how you buy for different product categories, eg. in-store vs. on-line
Many of these changes are not temporary adjustments where customers will fully revert to previous behaviour. To explore this, it is useful to start with customer segmentation from two perspectives. Firstly, understanding basic generational differences and secondly having a look at customer segmentation based on combinations of the four dimensions that generate understandable clusters of consumers. I will then overlay the Covid experience and then talk about post Covid behaviour.
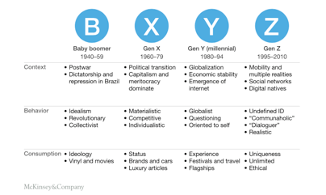
Starting with generational segmentation, McKinsey has put together a simple comparison of generational differences (Figure 2-2). Each generation has been brought up in a different contextual environment – political, economic, social, environmental and technological. That new context added to the specific context of our upbringing drives our behaviour and consumption patterns all other things being equal. Clearly, this representation in Figure 2-2 is very much a ‘Western’ or ‘industrialised’ world representation and applies less so to the developing world which live in very different socio-economic and political contexts.

Each of the generations are different in size and at any point in time have very different levels of overall consumption. Gen Z, although the smallest economic segment, are critical to understand as they are the generation most in tune with the current world. They are influencers that affect the direction of travel of the other segments with the closest segment, the Millennials, that will shift the most from their influence. The retired generation will shift the least.
Key components of Gen Z behaviour include:
- Adoption of technology – including the extensive level of home shopping and use of social networks. They are the first generation of truly digital natives.
- Social conscience – ‘Me Too’, ‘Black Lives Matter’, fair trade, ethical sourcing
- More experience oriented vs. product oriented
- Responsibility to the planet
Obviously, there are many other factors that affect consumer behaviour and as a result everyone in a generation does not behave in the same way. There are many different sources of analysis from all the consulting firms on how consumers segment in general; however, I chosen to pick some analysis that McKinsey has done that identifies 7 segments that group into the three themes of value, quality and image (Figure 2-3).
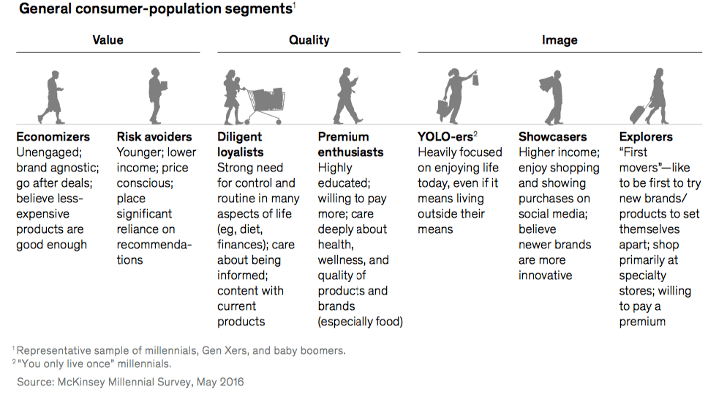
These segments mix attitudes with the practical links to individual situations including income/affluence, education and life stage. Within each segment here will be mixes of all generations; but, each generation will mix differently across the segments. The mix of these segments will also vary across countries.
Many companies will have done their own analysis and defined segments in a way that is relevant to their business and helps them successfully attract and acquire new customers. The more detailed and specific your understanding of your customers, the better you will be equipped to rapidly respond to changes in behaviour and be on the winning side of changes.
Let’s now look at the impact of Covid. For most of us there has been a big change in our behaviour, for many there has been a change in the current economics or future prospects of their household and for everyone they have had to take views (implicitly or explicitly) on their risk attitudes towards health and economic uncertainty (See Figure 2-4). These changes effectively add overlays onto any segmentation which will cause changes in clusters around key attributes and therefore create a new segmentation of customers.

Behaviourally, there has been a massive shift to on-line working, where possible, and on-line education that has been decided by others. In addition, there have been requirements to stay at home, limit time outside, and curb social get togethers. As a result, most people have adapted how they live in terms of solving how to work at home, being home educated, significantly increasing their at home eating and home fitness, etc. They have also gained time from the reduction in commuting time and other transportation time. The sum of these changes have driven new behaviours including home cooking, home fitness, remote shopping, on-line entertainment and on-line socialisation. These new behaviours are in turn also linked to a reprioritisation of where and how we spend our money and of course linked to changes in economic circumstances.
For most of us, we have now reached the 6 month level of changed behaviours and we are not back to a normal life with no restrictions, such as a return to commuting every day, in-person education, high levels of socialisation, visiting the gym and taking holidays in other countries without lockdown requirements on return. Shops, restaurants, offices, transportations systems etc. have not been adapted fully to accommodate a full return to our previous lives.
Economically, levels of unemployment have grown dramatically, and with those countries with furlough schemes growing levels of unemployment have to a large extent just been delayed. The increased unemployment is not spread evenly across the market; rather, it has hit the high street, the leisure and entertainment sector, the travel and tourism sector and parts of the health sector. It has also disproportionately affected women and the young. With uncertainty on the recovery of many businesses, especially in these sectors, many consumers face a period of economic uncertainty.
This overall experience has created heightened levels of both health and economic trauma. The health trauma will tend to be higher with the elder populations and those at risk. Although, there is large range of impact by country (using deaths per million as a measure, Figure 2-5), the trauma has also come from the level of measures imposed on a population by the government and the fear based media coverage on Covid. The perceived health risk is almost certainly higher than the actual risk on average; however, perception is reality for most people.

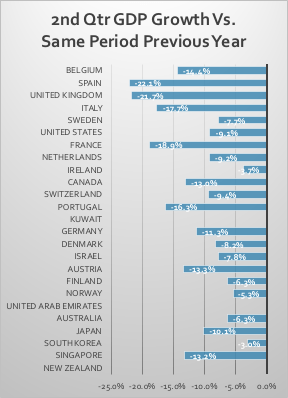
The economic trauma, which leads to uncertainty, has been pervasive with effectively all of the top 25 countries, based on GDP per Capita, seeing unprecedented declines in their second quarter year on year GDP growth (Figure 2-6). The economic declines are not necessarily linked to the health outcome of the Covid crisis; rather, they are much more related to the prevention and lock down steps taken by governments.
Although many countries are trying to move back towards normal, this is a slow process. There is pressure to maintain certain behaviours such as distancing; and, on and off lock downs are regular occurrences in countries as new pockets of Covid appear. We are a long way from being post Covid as there is no clarity on a vaccine, and therefore no clarity on the timing of the distribution of a vaccine. Finally, we are entering the flu season with a likely increased risk of further Covid challenges.
Moving on to how to think about changes in consumer behaviour going forward which will either be in a ‘living with Covid’ or a ‘post Covid’ world. The question is not will behaviours change but rather to what extent will they change. There are already clear structural drivers of change which include a significant economic impact to a large number of people from much higher unemployment in most countries and large permanent adjustments to working arrangements with many companies.
Analytically, consumer behaviour in a product or service sector or with a particular company are highly predictable by looking at four core variables – recency, frequency, monetary value and channel affinity. Here are the variable definitions:
- Recency – time since last purchase
- Frequency – number of purchases made over time
- Monetary value – total spend
- Channel affinity – preferred channel for purchases, which shops and in-person vs. on-line
Intuitively, these variables make sense as people to a large extent are habitual. They have routines, they repeat buy products or experiences they like, they become brand loyal as they build trust and become emotional engaged, and their choice of where to buy from is linked to their routines and convenience. On the flip side of these behaviours, is a general reluctance for many people to try something new, to buy in a different way, to try a different brand, and if you are in routines you expose yourself less to alternative products or choices. Clearly, there will be segments of people where these generalisations are less relevant; however, they are very relevant when looking at broad shifts in behaviour across segments of consumers.
The experience of the Covid lockdown has impacted all these variables. Restrictions on what we can do, where we can buy from and how we work coupled with health and economic uncertainty has significantly changed the behaviour of many people. As with all behavioural changes they can be positive, in total or for parts of the experience, or negative. The key to long term behavioural change is whether or not the Covid induced behavioural changes have provided rational or emotional benefits going forward. In the case of permanent structural changes (eg. your company moves to part-time remote work vs. all in person), the change in behaviour will naturally become the norm , with benefits being realised in different ways such as cost, time, convenience and performance.
The other part of behavioural change is to what extent the new valued behaviours have repeated and become habitual. Going back to the metrics of recency, frequency, monetisation and channel affinity, the longer the period of new behaviours being experienced, the stickier and more long lasting they will become.
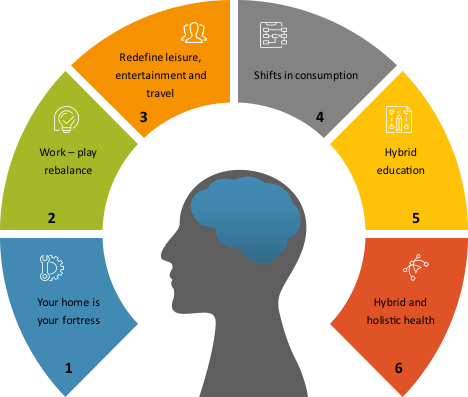
So, what does a review of available Covid related consumer research into behaviour change from either structural changes to markets, health and economic stresses and uncertainties, or new personal preferences indicate on potential behaviour change going forward – see the 6 themes identified in Figure 2-7.
On a personal level, what has happened for most people, perhaps excluding some Gen Z and some of the aged, is the increased pervasiveness and use of technology within our lives. Technology significantly impacts all of the 6 areas identified above. Many consumers have to some extent been forced to increase the rate of their adoption of technology across their lives. Consumer who only bought food in person are now doing a weekly shop online. Workers at home are more comprehensively using technologies (e.g. Zoom) for meetings and interactions and they are then using the same technologies for remote socialisation. Home fitness apps are being used as gyms have been closed. Core education is being conducted remotely. Higher levels of use of on-screen interactive games are being used as well as the use of services such as Netflix and Amazon Prime. Large numbers of consumers have now overcome their reluctance to use technology and experienced its benefits.
Looking now at each of the 6 themes:
‘Your home is your fortress’ – This is a place of safety in times of health risk. We should expect there is now a higher appreciation of home time and a clearer definition of what people want from their homes. Consumers have been increasing their investments in the technologies to be able to work, play and be educated at home. There are also some trends emerging of disproportionate DIY growth and I would expect that overtime there may well be higher levels of purchasing of other in-home products.
‘Work-play rebalance’ – With remote working now and clear trends towards more remote working going forward, this will free up significant amounts of commuting time for alternative use, e.g. fitness, entertainment, home cooking, etc.
‘Redefine leisure, entertainment and travel’ – Almost certainly there will be changes in the consumption mix of leisure, entertainment and travel; but how it plays out is very hard to predict. During lockdown and the subsequent restrictions there have been major short-term changes linked to home entertainment, reduction of the use of restaurants and bars, and minimisation of, or closer to home, travelling.
‘Shifts in consumption’ – Driven initially by lockdown there has a been a massive shift in consumption to on-line purchasing. A significant portion of this will have gone through Amazon who, in many countries, is involved in about 50% of all home shopping. It can be expected that not all of this will revert back to in person shopping. In a McKinsey study (“Understanding and shaping consumer behavior in the next normal.”, McKinsey & Company, July 2020) on consumers who tried grocery delivery for the first time during the Covid 19 crisis, more than 80 percent say they were satisfied with the ease and safety of the experience; 70 percent even found it enjoyable and 40 percent said they intended to continue to get their groceries delivered after the crisis. In many countries, such as the UK, for a period of time almost all clothing stores were closed and so there was also a dramatic shift to on-line purchasing of this product category.
Consumers have now bought products from new stores (on-line and in-person) so loyalties will have started to change, and new loyalties/habits will have started to occur after 6 months of the Covid 19 crisis. With hygiene, or health safety, now also being part of the purchasing decision, traditional large and crowded stores will tend be lower in the consumer choice of where to shop. In addition, with on-line purchasing, especially through Amazon, a traditional limited choice in a store has been replaced by massive selection options, and research is indicating that this is affecting historic brand loyalties. Another factor that will affect historic brand loyalty are the Covid induced economic stresses and uncertainty which is driving swathes of consumers towards more cost-value product selection. Finally, the combination of visible local economic turmoil coupled with growing climate and social responsibility concerns is expected to accelerate a shift to local produce and green and ethical products.
‘Hybrid Education’ – Almost all children, with involvement of their parents, and university students have been forced to try some form of on-line education. Some of it will have been successful and some unsuccessful; nevertheless, it will have built further comfort with the use of technology for education. Many will have looked beyond their schools to supplement their learning and tried what has been available on-line for a number of years and provides a more advanced and appropriate technology based educational experience. For K-12 (Kindergarten to grade 12) education they may have tried the Khan Academy or for university or further education they may have tried edX, Coursera, or Udacity. New and improved on-line experiences are arriving on the internet continuously and will challenge poor face to face experiences or augment this traditional learning mode. Enhancing its continued adoption will be the low cost or free use access to these quality educational applications.
‘Hybrid and holistic health’ – This pandemic has brought a strong awareness to our health. The linkage of Covid 19 risks to those with ongoing health problems (e.g. heart, diabetes, asthma, etc.) has brought to light the importance of wellness. There has been dramatically increased use of digital wellness apps (yoga, circuit training, etc.) and also increases in the purchase of at home fitness equipment. More people are walking or riding bicycles and reducing their use of public transport. In traditional medical health, we have been forced to have on-line medical appointments as in many countries doctors will not initially see you in person. Once again, with the 6 months of new habits forming supplemented by the high levels of media identifying concerns with the upcoming flu season, an increased focus on wellness and prevention and further growth of on-line medical should be expected.
I have not seen any in-depth research that provides real insights into the scale of change to a ‘new normal’ and there is more to learn as we continue to live in this pandemic. The consulting companies through their sampling have pulled together their sense of segmentation of post Covid customers which I think is useful to consider but each company needs to pull together its own views and then though ongoing analytics refine their own segmentation. Just as an example here are the segment names defined by three consulting companies – Accenture, McKinsey, EY. The names help you visualise the segments and you can see the overlap between the alternative segmentations.
- Accenture – ‘the Worrier’, ‘the Individualist’, ‘the Rationalist’, ‘the Activist’, ‘the Indifferent’
- McKinsey – ‘Affluent and unaffected’, ‘Uprooted and ‘unemployed, ‘Financially secure but anxious’, ‘Out trying to make ends meet’, ‘Disconnect retirees’
- EY – ‘Get to normal’, ‘Cautiously extravagant’, ‘Stay frugal’, ‘Keep cutting’, ‘Back with a bang’
What we do know is that the longer restrictions and forced changes in behaviour last, the more likely future behaviours will at least reflect the positive experiences of the changed behaviours. It is also clear that the rate of adoption of new technologies across the generations has accelerated and this will stimulate further investments to improve the related experiences. Cycles of innovation and adoption will accelerate as a result of this pandemic. For many consumers, usually of an older age, they may not have bee able to delay the adoption of certain technology applications; and therefore, will likely be more comfortable trying new applications going forward.
For business, the pandemic disruption has now caused us to go into a period of non-linear change across many parts of our lives. This means business need timely data and analytics to identify changes in demand and the growth of new opportunities. They will also need the agility and flexibility to respond and take advantage of new market opportunities or to minimise the costs of current activities that will no longer be profitable. As noted earlier, these non-linear changes will be driven by a combination of:
- Structural responses by businesses to Covid. For example, policy shifts by companies towards remote working will make changes to consumer spending and ripple through to the retail and service sector around offices.
- Structural responses by governments. For example, rules and regulations on crowds and distancing, or adjustments related to public transport and other types of infrastructure.
- The overlaying onto customer segmentation of behavioural changes linked to actual and perceived health risks of consumers
- The additional overlaying of economic changes and uncertainties to large sets of consumers
- Changes in the attitudes of sets of people with respect to buying locally as a response to seeing local economic distress in combination with a sense of social responsibility and increased climate change concerns
- Responses by the government to address potential future health challenges and alleviate the economic recession we have entered. As an example, this would include accelerated investment in moving a country towards ‘greening’ the economy and society.
- The rate of change of adoption of existing technology applications and introduction of new technology applications
I will talk more about some of these factors in the next blogs. These blogs will get into more detail on how businesses can be more effective at responding to this changing situation and also the role of the government.
#Covid 19 #pandemic #post Covid #strategy #disruption #resilience #innovation #consumer segmentation #consumer behaviour #GenZ #millenials #baby boomers #WHO #sustainable development goals #McKinsey #Accenture #EY #UN SDGs #WEF #blacklivesmatter #metoo #DoughnutEconomics @Kate Raworth